If you’re having networking or internet issues, it might be time to change your DNS server settings. Or perhaps you just want to switch to a faster DNS provider that is more reliable and secure? Regardless of the reason, changing your DNS settings on Windows 10 and Windows 11 is simple, with several different methods to get the job done.
What is DNS?
DNS, short for Domain Name System, resolves domain names and network resource names into their respective Internet Protocol (IP) addresses. IP addresses are unique numbers given to networkable devices like computers, cellphones, smart devices, and domains that allow them to communicate and transmit data with one another. An example of an IPv4 address is 104.16.210.88.
DNS is important because it allows people to use domain names like www.pdq.com and network resource names like FILE-SERVER01 instead of IP addresses, which are more difficult to remember. When a user tries to navigate to a website or network resource using a name, DNS is queried and returns the corresponding IP address that can then be used to navigate to the correct destination. This process happens seamlessly and in the background, which is my favorite way for processes to happen.
To learn more about DNS, check out our ultimate guide to DNS.
Why you should consider changing your DNS server settings
DNS is a core component of the internet and networks around the world. As such, there are several reasons why you may want to learn how to change your DNS server settings.
Faster DNS resolution
Most internet-connected devices automatically use the DNS servers designated by their internet service providers (ISP). For example, if your ISP is Comcast, it automatically directs you to its DNS servers at the IP addresses 75.75.75.75 and 75.75.76.76. However, switching your settings to a faster DNS server could boost your web browsing performance. Consider using a free Windows utility, like DNS Benchmark, to find the best-performing DNS servers for you.
Privacy concerns
In our modern, always-connected society, our privacy is constantly at risk. And while limiting our compulsive social media habits would significantly reduce that risk, even DNS provides a means for service providers to collect our DNS queries, which can be used to establish a user profile.
If privacy is a concern, I recommend looking into the privacy policy of various DNS hosts to find one that meets your privacy expectations.
Reliability
Reliability is a major concern when it comes to DNS. An unreliable DNS server can result in slow, unresponsive DNS queries and ultimately lead to a loss of internet connectivity. When deciding which DNS server to use, pick one from a reputable provider with high availability and redundancy.
How to change DNS server settings using Control Panel
Configuring your DNS server settings with Control Panel is quick, easy, and probably the oldest method on this list. Best of all, this approach works on both Windows 10 and Windows 11 devices. While Microsoft seems determined replace Control Panel with the new Settings app, they’ll have to pry it out of my cold, dead hands.
1. Enter control panel into the Windows search bar, then click on the Control Panel app.
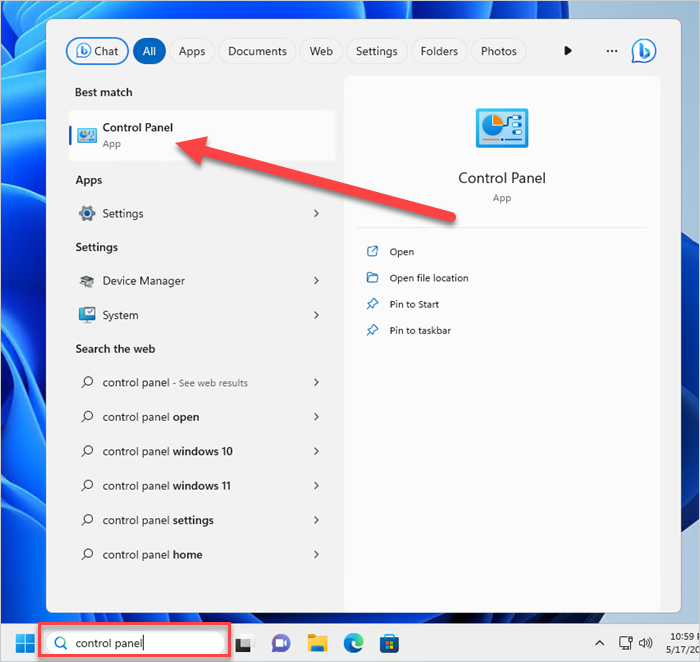
2. Click on View network status and tasks.
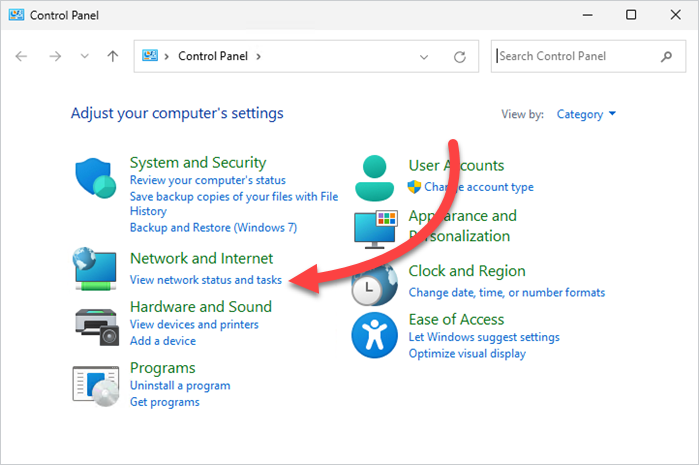
3. Click on the name of your connection next to the Connections: field.
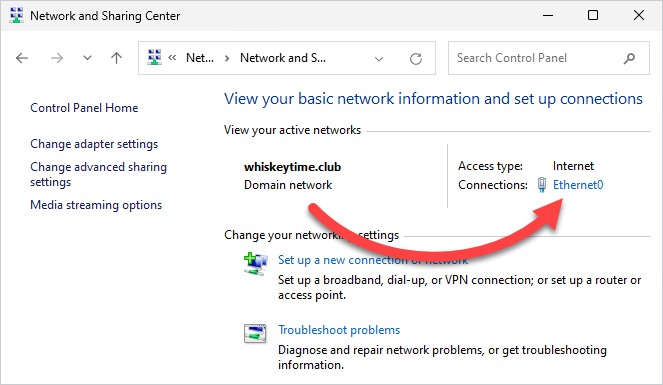
4. In the status window, click Properties.
5. In the properties window, select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), then click Properties.
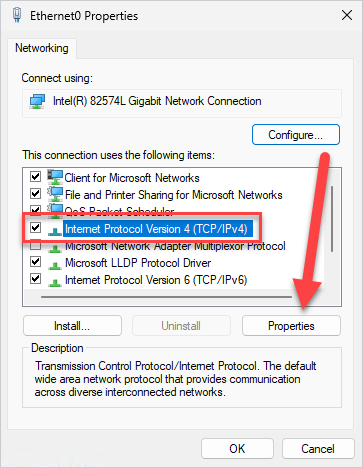
6. Select Use the following DNS server addresses: and enter the IP addresses of the DNS servers you want to use. Here are a few popular servers that you can try.
OpenDNS: 208.67.222.222 & 208.67.220.220
Cloudflare: 1.1.1.1 & 1.0.0.1
Google: 8.8.8.8 & 8.8.4.4
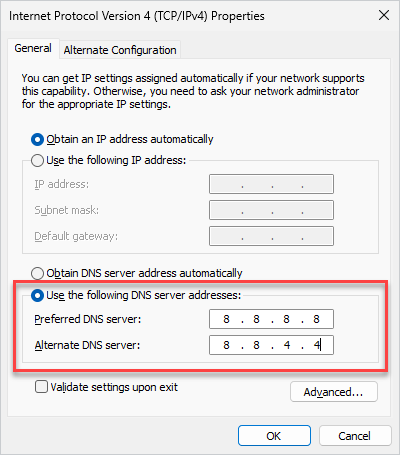
7. When you’re finished, click OK, then close the Properties and Status windows.
That’s all there is to it. You’ve successfully changed your DNS server settings. However, continue reading to learn about the newer methods, especially since Control Panel may disappear in future versions of Windows.
Keep endpoints patched & secure
Deploy custom or prebuilt software packages, automate maintenance tasks, and secure your Windows devices — no matter where they are.
How to configure DNS server settings in the Windows 10 Settings app
Microsoft is transitioning all the settings away from Control Panel and into the Settings app. In Windows 10, the Settings app contains many — but not all — of the configuration options found in Control Panel. As a result, this method uses a combination of both the Settings app and the Control Panel.
1. Click on the Windows button.
2. Click on the Gear (settings) icon.
3. Click Network & Internet.
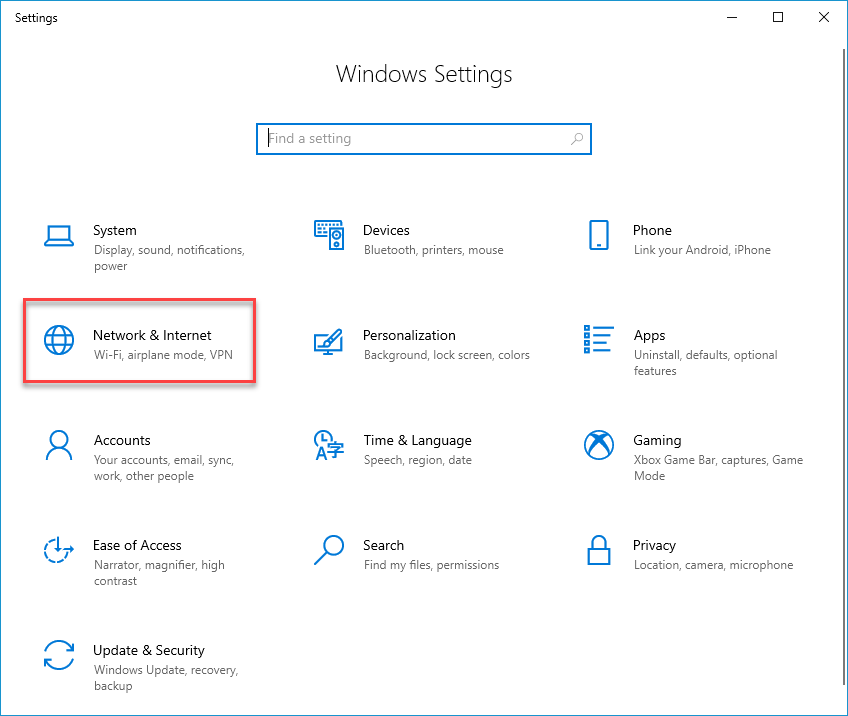
4. Click Change adapter options.
5. Double-click on your adapter.
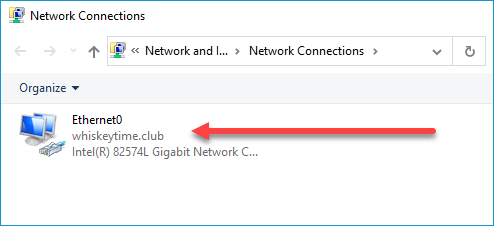
6. Repeat steps 4 through 7 of the previous method.
While this method works, transitioning from the Settings app to Control Panel feels a bit clunky.
How to change DNS settings on Windows 11
The Settings app in Windows 11 has drastically improved over the Windows 10 version. It’s easier to navigate, and you can configure most settings directly within the Settings app, including your DNS settings. Here’s how to change DNS servers using the Settings app in Windows 11.
1. Right-click on the Windows button, then click Settings.
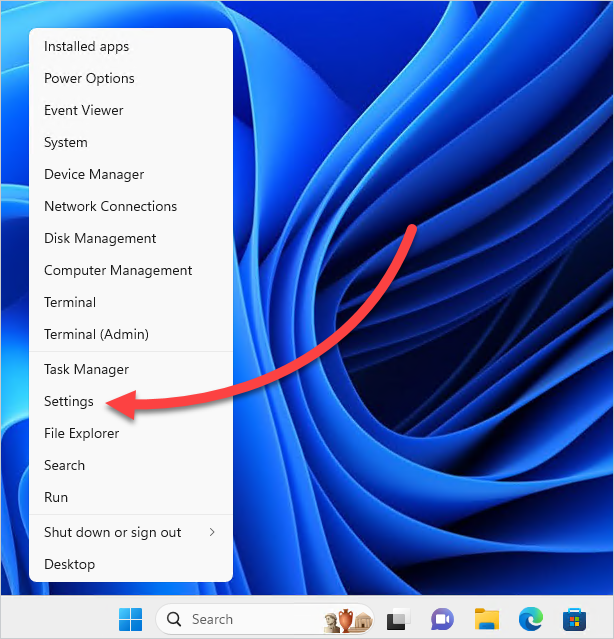
2. Click Network & internet.
3. If you are using Wi-Fi, click Wi-Fi, click Hardware properties, then click Edit next to DNS server assignment. If you are using an ethernet connection, click Ethernet, then click Edit next to DNS server assignment.
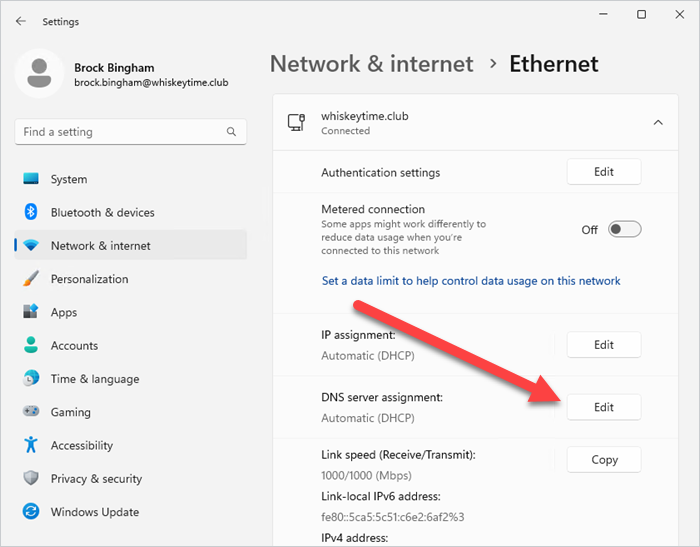
4. Using the drop-down menu, select Manual, then toggle IPv4 to On.
5. Enter the Preferred DNS address and the Alternate DNS address, then click Save.
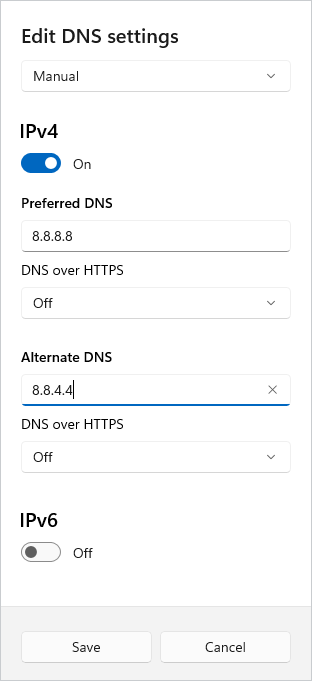
While the Settings app in Windows 10 was a bit cumbersome, Microsoft significantly improved it in Windows 11, and it might be the quickest way to configure your DNS settings.
How to set your DNS settings with PowerShell
PowerShell continues to grow in functionality and popularity. With the right PowerShell commands, there’s not much you can’t accomplish, and that includes modifying your DNS settings.
If you’re new to PowerShell, don’t worry. This method uses pretty basic commands, and we’ll walk you through the entire process.
1. Right-click on the Windows button and click Windows PowerShell (Admin). If you’re using Windows 11, click Terminal (Admin).
2. Click Yes if prompted by a User Account Control dialog box.
3. At the PowerShell prompt, input the following command:
Get-NetIPConfiguration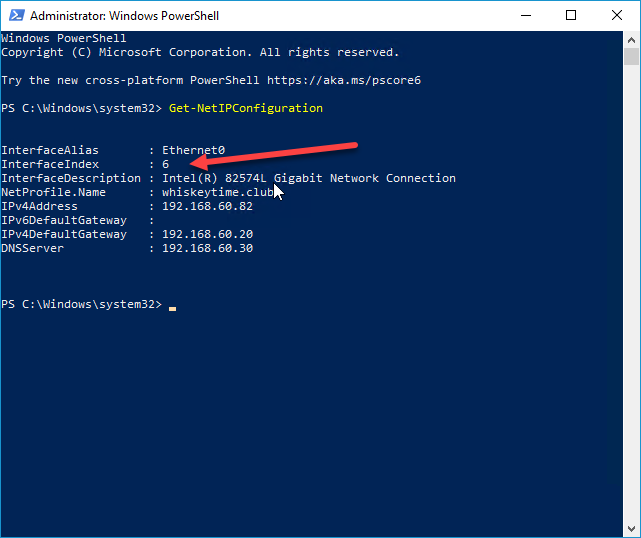
4. Make a note of your InterfaceIndex number. In the image above, my InterfaceIndex is 6.
5. Enter the following command replacing your InterfaceIndex number and the server address you wish to use:
Set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceIndex 6 -ServerAddresses 8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.46. Ensure the settings have been changed by re-entering the command: Get-NetIPConfiguration
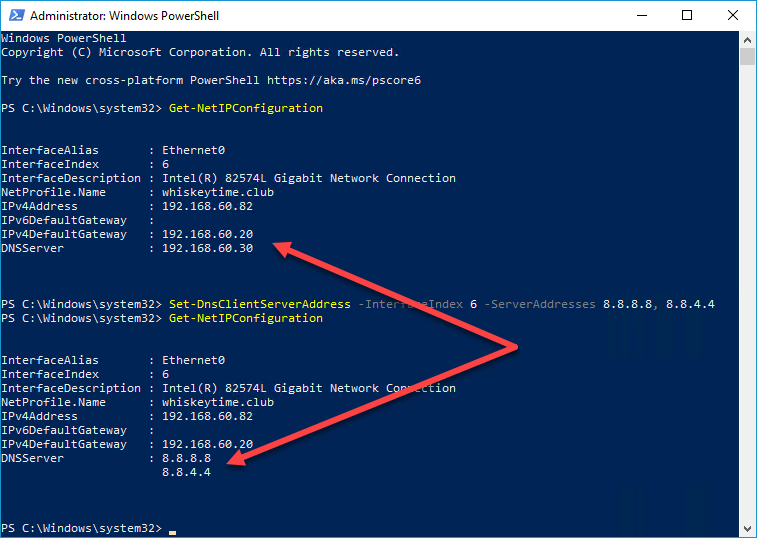
As you can see, our DNSServer was changed from 192.168.60.30 to Google’s DNS servers, 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4. Now that you know how to change your DNS server using PowerShell, check out The PowerShell Podcast to discover all the other awesome things you can do with PowerShell.
It’s always DNS
Sysadmins have a saying. It’s not DNS. There’s no way it’s DNS. It was DNS. Hopefully this guide helps reduce your DNS woes so you can have a smoother, faster, and more secure online experience. Just keep in mind that a better DNS server isn’t going to stop you from posting an embarrassing picture on social media. That one’s on you.